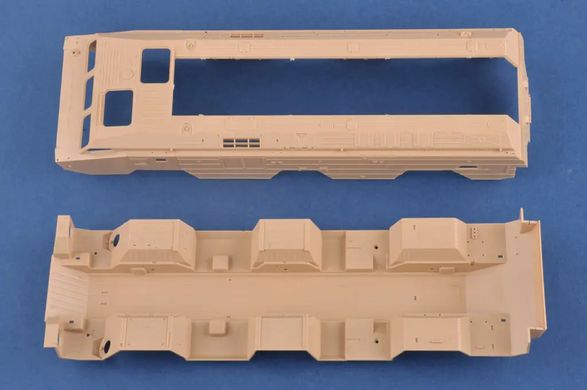
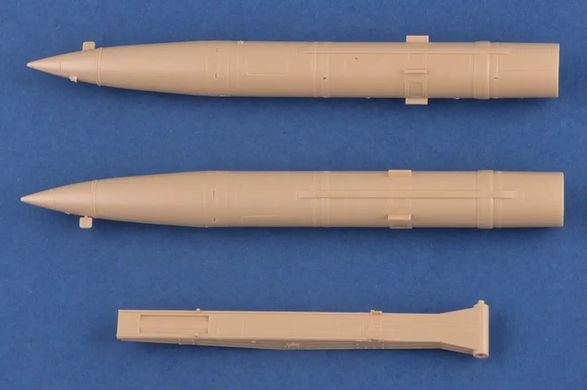
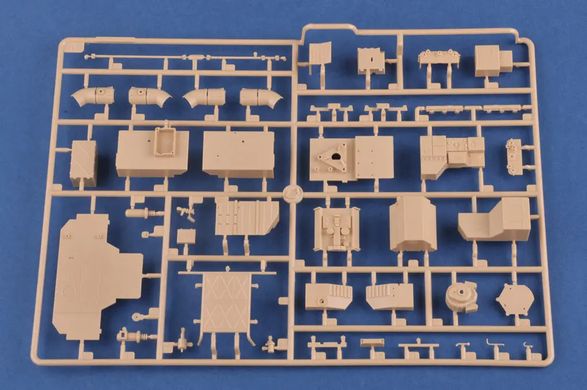
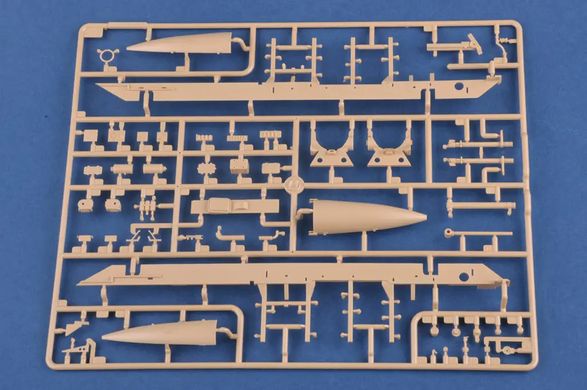
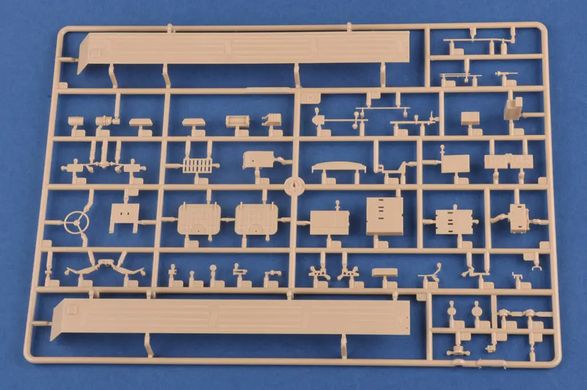
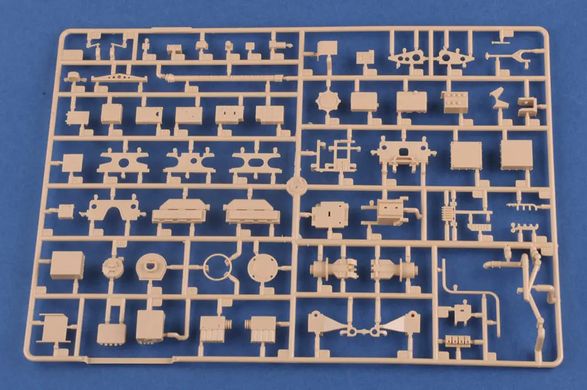
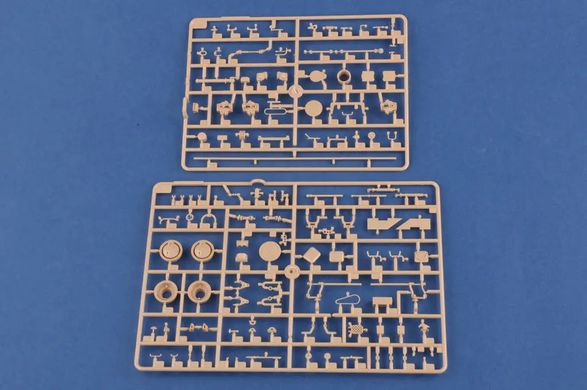
The 9K79 Point (NATO code: SS-21 Scarab) is a Soviet and now Russian tactical missile launcher on a wheeled platform that uses the 9М79 family of missiles. The length of the projectile is 640 cm with a diameter of 650 millimeters. The take-off weight reaches 2,000 kilograms, and the missile can carry a warhead weighing up to 482 kilograms, including tactical nuclear warheads with a capacity of 10 kT. The range of the missile in the Scarab B version is probably up to 120 kilometers. Research and development work on the Toczka 9K79 missile complex began in the mid-1960s. Initially, a radio command guidance system was created, but it was abandoned relatively quickly and the goal was to create a "shoot and forget" missile with an inertial guidance system. Finally, the new missile complex began to enter service in 1978-1979, and on a larger scale - from 1981. Initially, this type of weapon was used at the level of divisions, but over time they began to be created as independent brigades. The 9K79 Toczka was also exported to Warsaw Pact countries, including Poland. It entered our armed forces in 1987, and was decommissioned in 2005. The 9K79 Toczka missile system is designed to destroy surface targets, such as ammunition depots, as well as point targets, such as enemy fire pits. Weapons were used in battles, among other things,